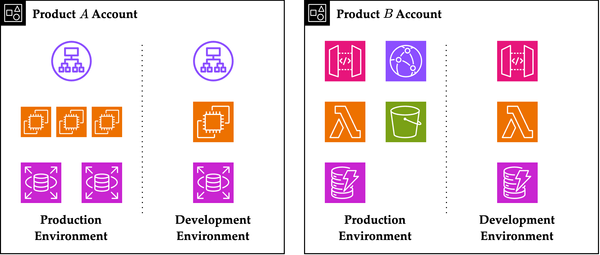
Secure IAM on AWS with Multi-Account Strategy
Benefits of multi-account strategy on AWS and how to achieve operational excellence on multi-account structures

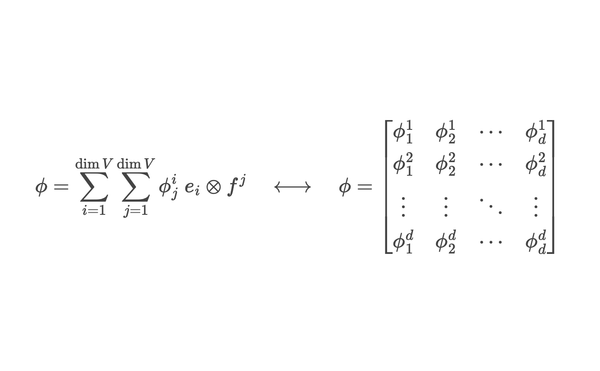
The deep reason behind the strange definition of matrix multiplication
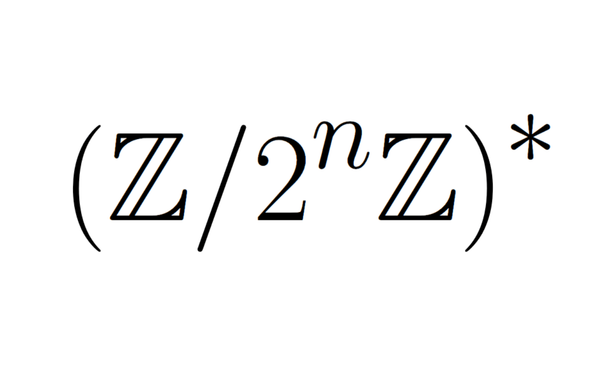
Why CKKS rotations use automorphisms $x \mapsto x^{-1}$ and $x \mapsto x^{5^k}$
마크다운에서 수식을 사용하는 것이 어려운 이유와 해결 방법
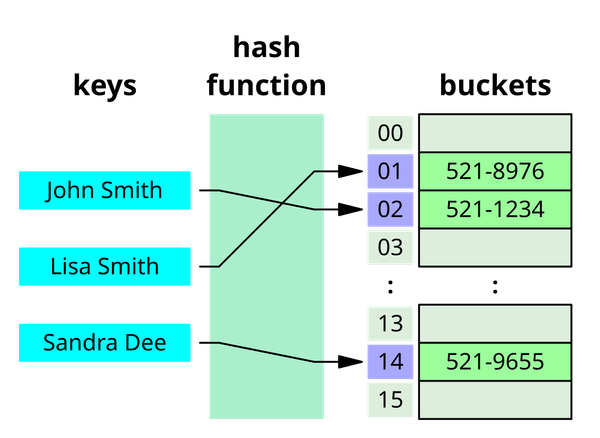
Expected time complexities of the search operation in hash tables using chaining or open addressing

How to be a great researcher!

Benefits of multi-account strategy on AWS and how to achieve operational excellence on multi-account structures
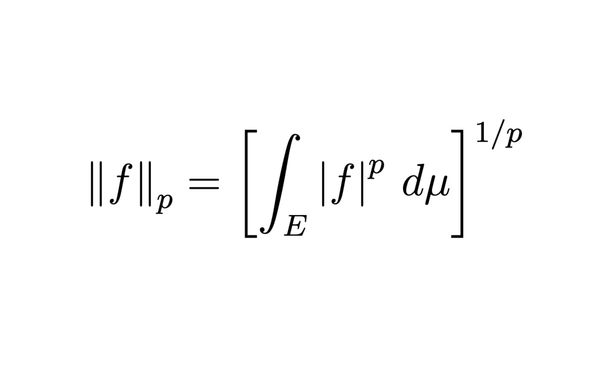
$\mathcal{L}^p$ functions and their properties
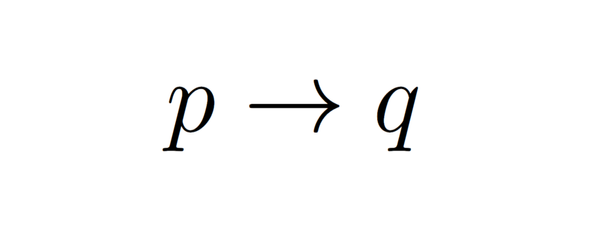
List of proofs with Coq for each rule of inference stated in Wikipedia
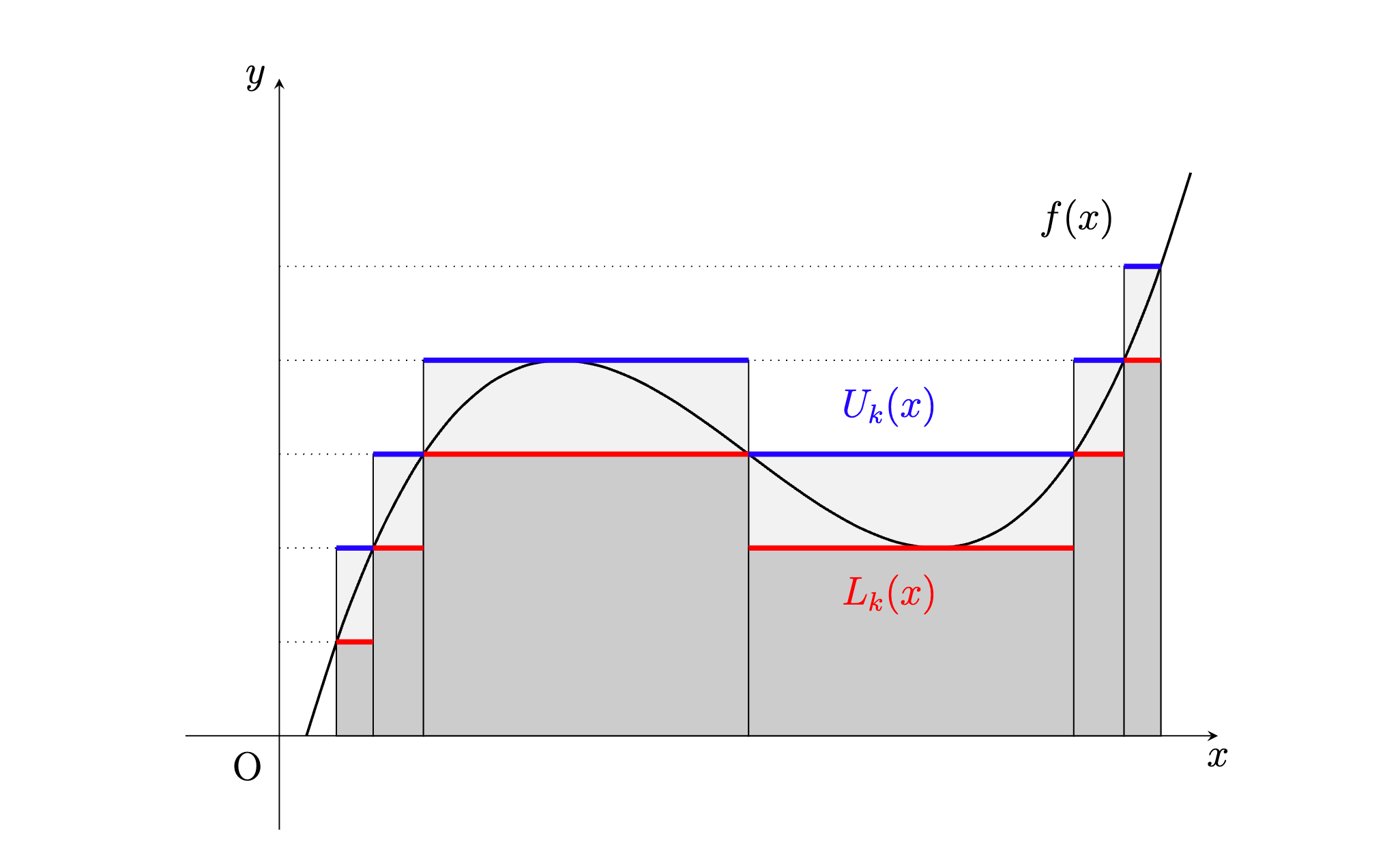
Lebesgue vs Riemann integral
Almost Everywhere 지난 글에서 measure가 0인 집합 위에서 적분하면 결과가 0이 됨을 확인했습니다. 적분 입장에서 보면 measure가 0인 곳에서의 적분은 의미가 없다고 생각할 수 있겠죠? 그러면 앞으로 그런걸 무시해도 된다고 하면 어떨까요? 정의. (Almost Everywhere) $P = P(x)$ 가 어떤 성질이라 하자.[1] 만약 measure가 0인 집합 $N$이 존재하여
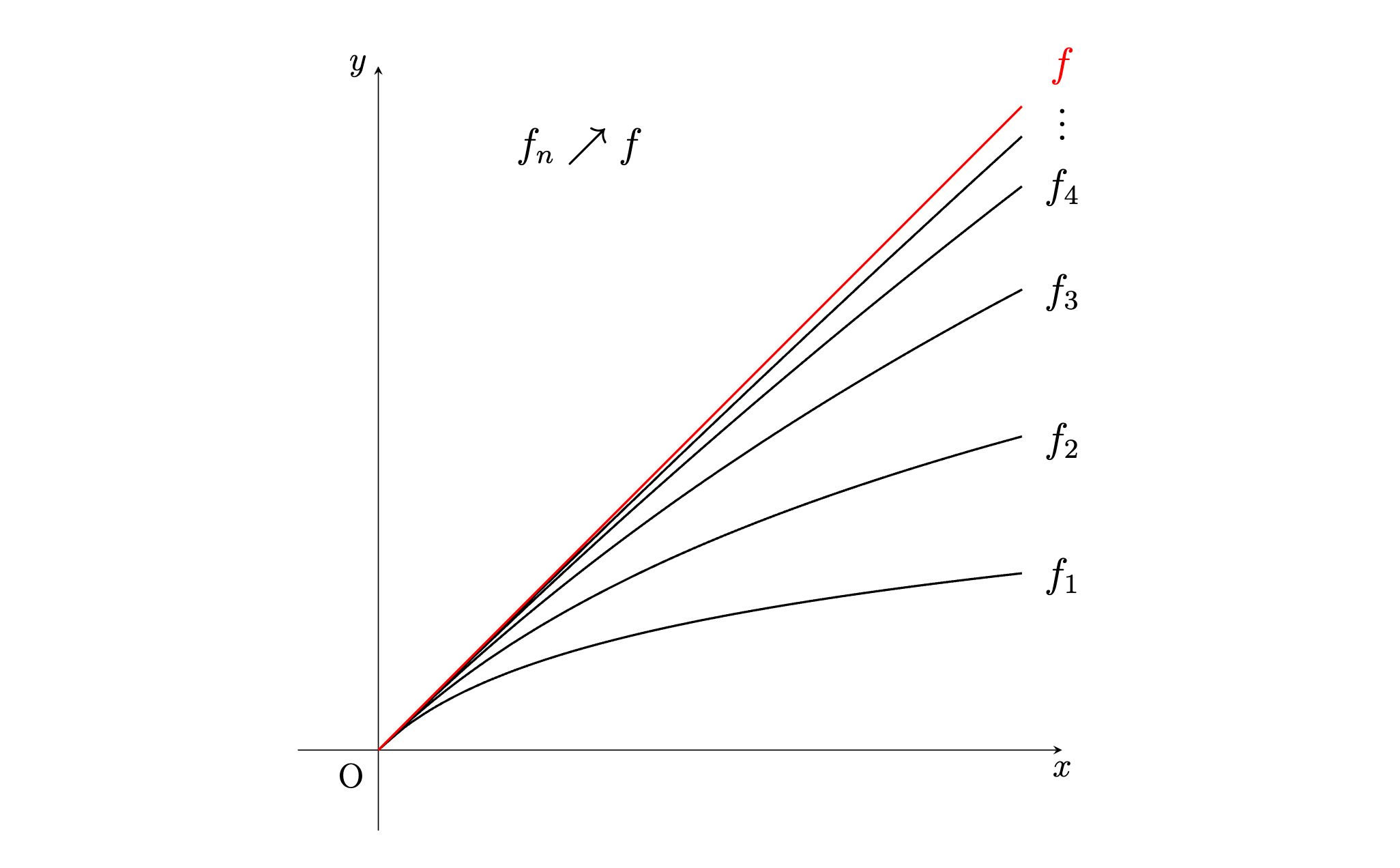
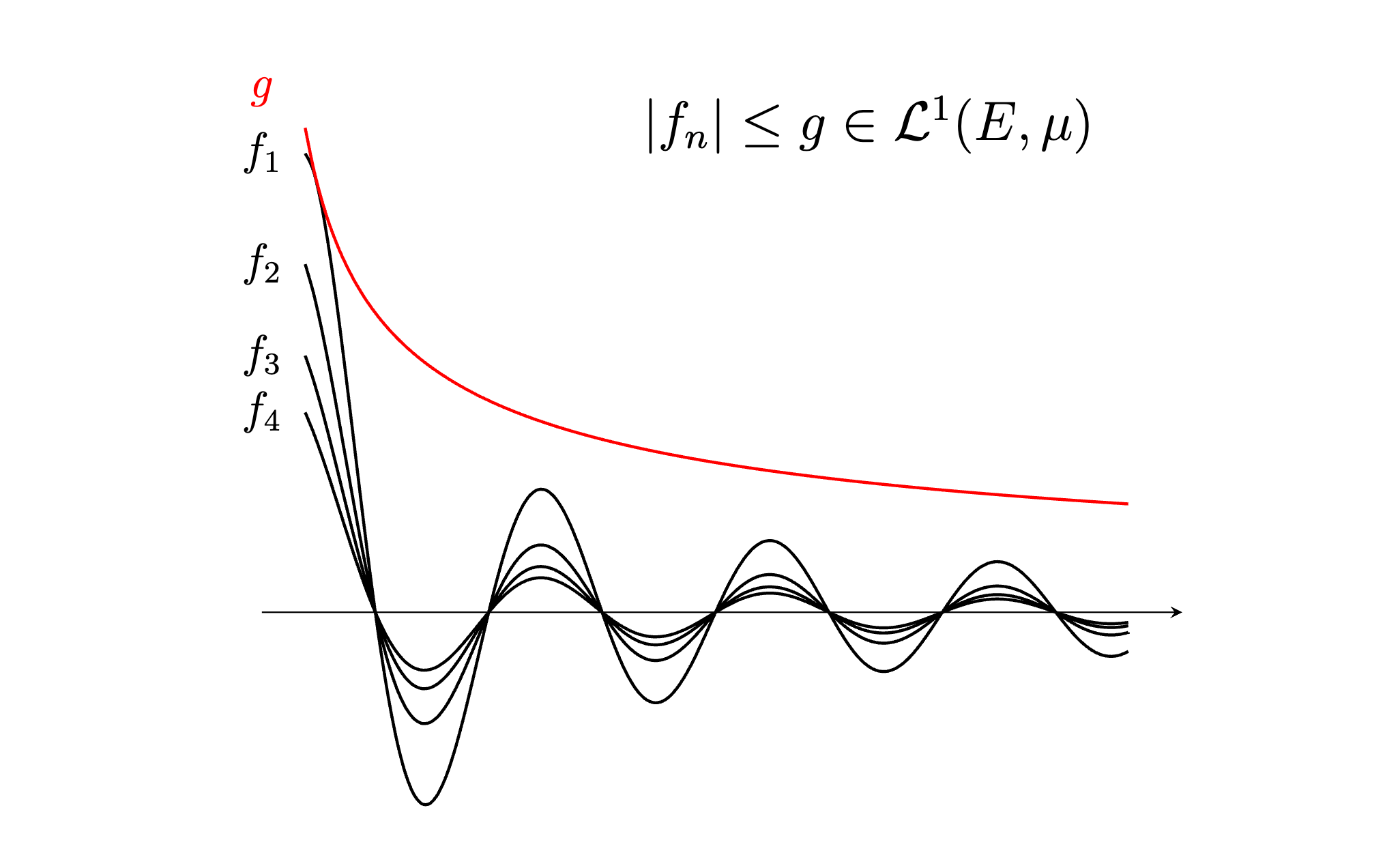
르벡 적분 이론에서 굉장히 자주 사용되는 수렴 정리에 대해 다루겠습니다. 이 정리들을 사용하면 굉장히 유용한 결과를 쉽게 얻을 수 있습니다. Monotone Convergence Theorem 먼저 단조 수렴 정리(monotone convergence theorem, MCT)입니다. 이 정리에서는 $f _ n \geq 0$ 인 것이 매우 중요합니다. 정리. (단조 수렴 정리) $f _ n: X \rightarrow[
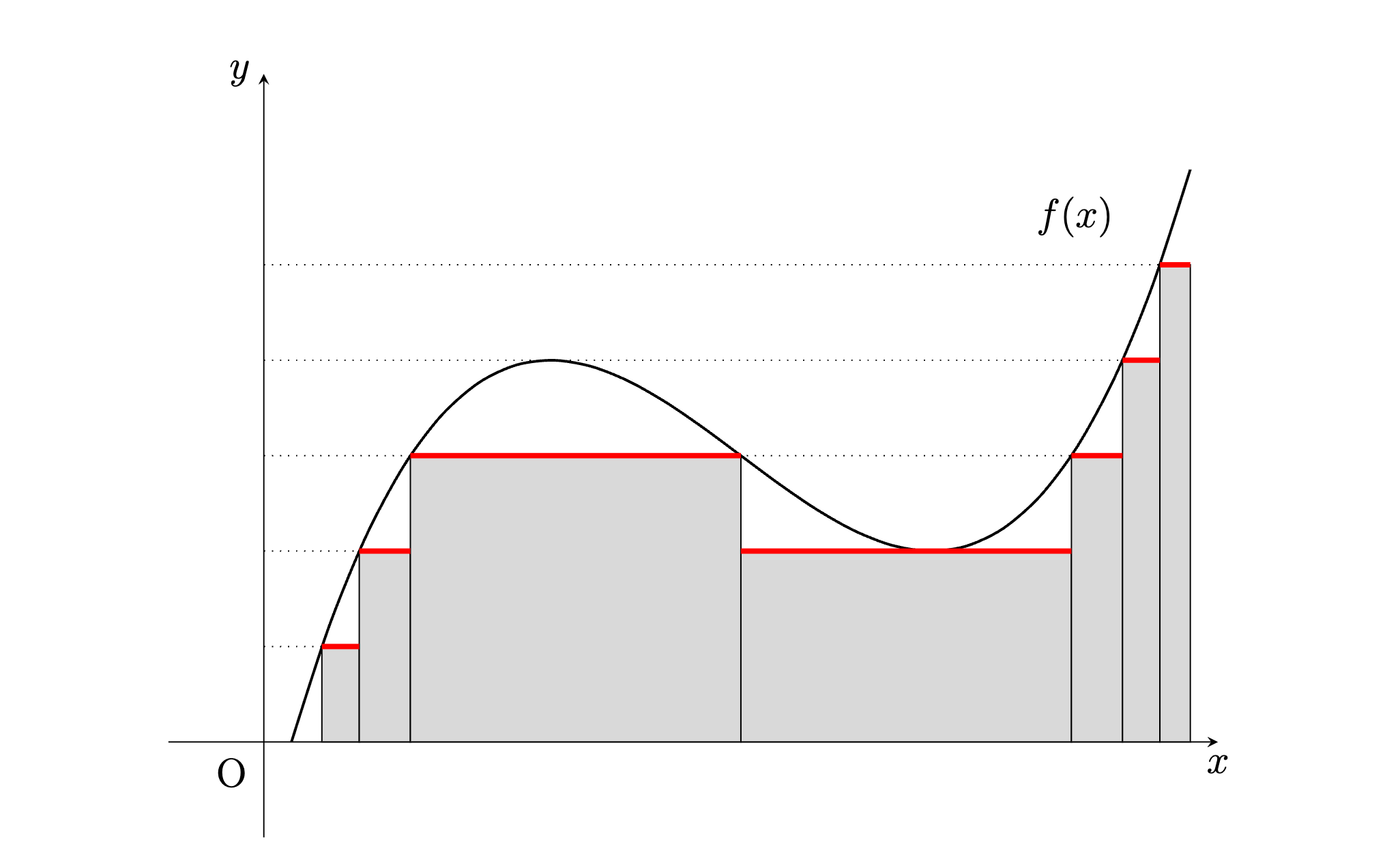
Lebesgue Integration 르벡 적분을 단계적으로 정의하려고 합니다. $X = (X, \mathscr{F}, \mu)$ 라고 계속 가정합니다. $\mathscr{F}$는 $\sigma$-algebra on $X$, $\mu$는 $\mathscr{F}$의 measure 입니다. $E \in \mathscr{F}$ 일 때, 적분을 정의하기 위해 $$\mathscr{F} _ E = \lbrace A \cap E : A \in \mathscr{F}\rbrace,